Interactions among end user, data, information, and decision-making?
It is the end user who must analyze data to produce the information that is later used in decision making. Most business decisions create additional data that will be used to monitor and evaluate the company situation. Thus data will be, or should be, recycled in order to produce feedback concerning an action’s effectiveness and efficiency. Below is a simple diagram of one of today’s data giants, facebook: As you can see below, the user’s interactions creates and also renders data from the server depending on their actions and inputs.
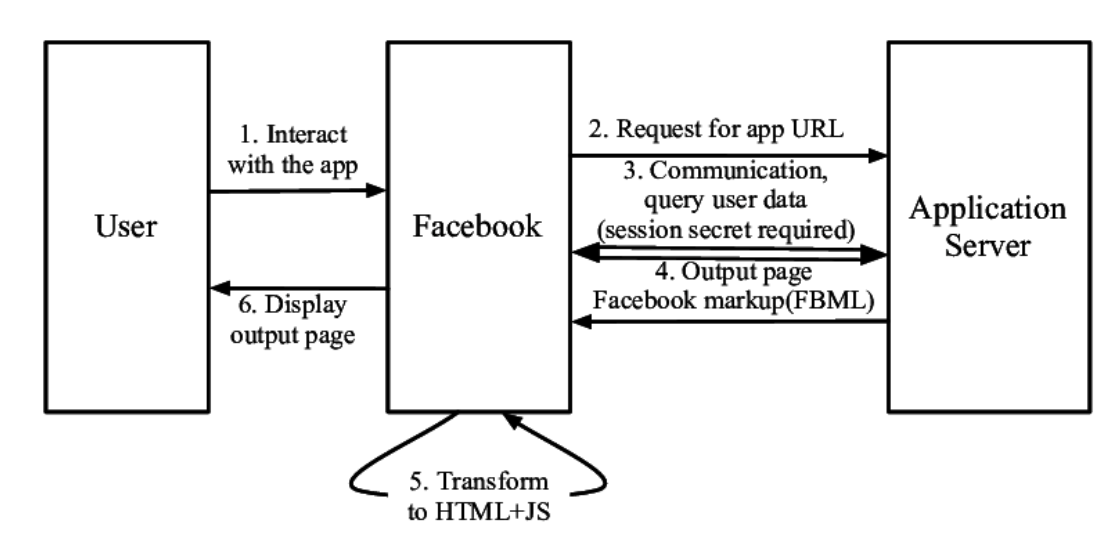
Depending larger on the application, it’s design and functionality, the interactions and data flow could very. Typically in consumer facing web applications, the end user is engaging with the application by inputting various types of information that would be stored as data somewhere on the server, and called upon and used during a different stage of the application and user experience. Many web applications these days using ‘MVC’ method or Model-View-Controller, software pattern; the Model-View-Controller is an architectural type pattern that separates an application into three main logical components: the model, the view, and the controller; each of the components are developing to handle specific development aspects of an application. This is relevant because, through MVC, this is done to separate internal representations of information from the ways information is presented to and accepted from the user.
SUPPOSE THAT YOU ARE A DBA. WHAT DATA DIMENSIONS WOULD YOU DESCRIBE TO TOP-LEVEL MANAGERS TO OBTAIN THEIR SUPPORT FOR ENDORSING THE DATA ADMINISTRATION FUNCTION?
The number one step would be to reiterate the importance of data as an organization asset, to be handled just as any other asset. High end managers should understand this critical notion and should be willing to commit organization resources to handle such data as a company asset. A next step would be to identify and articulate the need for, and role of the DBMS in this said organization. Managers and end users alike must understand how the DBMS can enhance and help the work of the company at all many levels; top tier management, middle tier management, and as well as operational. Lastly, the impact of a DBMS introduction into a company should be broken down and explained; particularly the more technical, manager style, and cultural parts of said process. It would be important to illustrate the dimensions and processes through a Business Systems Analysts to illustrate value to higher up executives and managers.
DESCRIBE AND CONTRAST THE INFORMATION NEEDS AT THE STRATEGIC, TACTICAL, AND OPERATIONAL LEVELS IN AN ORGANIZATION. USE EXAMPLES TO EXPLAIN YOUR ANSWER.
Strategic planning is a company process of outlining its strategy, direction, and decision makings on allocating real resources to pursue strategy. In general, strategic planning handles, on the entirety business, rather than just a narrowed unit, with at least one of the following three prime questions; “What do we do?”, “For whom do we do it?”, “How do we excel?”. For instance, the number one and number three questions are ones that motivate an acquisition. Acquisitions are alas strategic decisions. Generally strategic decisions look at three to five years, although many extend the vision to around twenty years, or longer term. Because of this time horizon and the style of the questions dealt, errors potentially occurring during the execution of a strategic plan are afflicted by large uncertainties and would lie remotely out of the control of management; war, geopolitical shocks, etc.. These errors, in joint with the potential consequences are coined “strategic risks”. Missed opportunities could also be seen as strategic risks. Tactical planning is shorter style range planning reiterating the current operations of many different parts of the company. Short range, is typically illustrated as a range of time extending close to twelve months or less, in the future. Managers take advantage of tactical planning to illustrate what the many parts of the company must do for itself to be successful at a point of one year or less, going forward. Tactical plans are almost always coordinated in the areas of production, marketing and personnel, finance and also, plant facilities. Because of this time horizon and the nature of the questions dealt, errors possibly happening at the execution time of a tactical plan should be covered by some uncertainties and may live closer to the control of management; following year shipping prices, energy consumption rates, etc. So again, these error types, in joint to the potential consequences are called “tactical risks”.
So, operational planning is simple procedure of linking strategic objectives to tactical ones, and it’s objectives. It illustrates milestone points, conditions for success and failure, and would describe how, or what aspect of, a strategic plan would be set into operations during a set period. An operational plan would identify four main questions: ”Where are we now?”, “Where do we want to be?”, “How do we get there?”, and then “How do we measure our progress?”. Operational risks are these arising from the persons, systems at hand, and processes during which an organization operates and may include several other classes of risk; fraud, legal, physical, and or environmental type risks. Operational risks are the risks deriving from unsatisfactory or failed internal type processes, people, as well as systems, or from the many external events that could occur; man-made or natural hazards, for instance. An open pit slide, a power black-out (no matter naturally or man-made), and then explosions in a process plant are all types operational hazards generating operational risks, etc that could easily exist.
DESCRIBE THE DBA’S RESPONSIBILITIES.
The database administrator, or DBA for short, is the individual responsible for the handling and management of the shared database within a company or organization. The DBA controls the DB (database) administration side function within the company. This DBA is to be responsible for handling the overarching corporate data resource, computerized and non-computerized ones. Alas, the DA would be given a larger degree of responsibility as well as authority than said DBA. Pending on company style, both the DBA and the DA roles may touch and could even be joined in a single type role or individual. The DBA role would require both managerial and technical style skill sets. More roles of the DBA, would include; establish and maintain sound backup and recovery policies and procedures, handle care of the Database design and it’s implementation, implement and alas maintain database security (creating and maintaining users and roles, assigninging privileges, etc), the database tuning and performance observing.
WHY AND HOW ARE NEW TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCES IN COMPUTERS AND DATABASES CHANGING THE DBA’S ROLE?
Like many roles in technology; the DBA’s role is constantly changing, adapting and evolving. “The DBA’s Technical Role” could tie the discussion of the increasing use of web applications. The DBA’s function is potentially one of the most dynamic functions of any company. New technological enhancements continue to change the DBA function. For instance, each of the following has an effect on the DBA function: the development of the DDBMS, development of the OODBMS, increasing use of LANs, rapid integration of Intranet, and Extranet applications, and their effects on the database design, implementation, and management. Also, security issues would become more so important. The basic role of a database administrator is to stash and handle the information in a database. They are alas responsible for reviewing the contents in the database. They are performing all the duties related to maintaining said database and are responsible for designing, and implementing the database. Additionally, they are responsible for taking back-ups of data regularly and to prevent from potentially unauthorized access attempts. They could be also known as DatabaseCoordinator or Database Programmer in some circles.
WHAT ARE THE TYPICAL ACTIVITIES INVOLVED IN THE MAINTENANCE OF THE DBMS AND ITS UTILITIES AND APPLICATIONS? WOULD YOU CONSIDER APPLICATION PERFORMANCE TUNING TO BE PART OF THE MAINTENANCE ACTIVITIES? EXPLAIN YOUR ANSWER.
Database (DB) performance tuning is an aspect of it’s maintenance activity. As the database system goes into operation, the database begins to expand. Resources would initially be assigned to the application, which are sufficient for the beginning loading of the said database. As the system would grow, the database would become even larger, and then the DBMS would require more resources to handle the growing demands at all times. Also; database performance would naturally go down as the database expands and more users take access to it. DBMS is essentially a software or application package that controls the creation, edition, updating, and manipulation of databases in a system. By DBMS, various databases can be developed at ease. It also allows various processes to simultaneously access various databases and records. Various DBMS make use of query applications which are essentially an example of functional developing high level languages. Yes; I would consider application performance tuning to be apart of maintenance as it’s a form of maintaining integrity in the system.
References:
Let’s define Strategic, Tactical and Operational planning. (2016, March 23). Retrieved from https://www.riskope.com/2014/04/03/lets-define-strategic-tactical-and-operational-planning/.
Coronel, C., & Morris, S. (2015). Database Systems: Design, Implementation, and Management (11th ed.). : Cengage Learning.
Databases. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.tutorialspoint.com/index.htm
McKendrick, J. (2019, April 11). The Changing Role of the DBA in the Expanding Cloud World. Retrieved from http://www.dbta.com/BigDataQuarterly/Articles/The-Changing-Role-of-the-DBA-in-the-Expanding-Cloud-World-131122.aspx.